Introduction
당시 neural network가 발전함에 따라서 RL에도 그대로 DL을 적용하고자 시도함
그러나 여러가지 문제점이 많이 존재
- The delay between actions and resulting rewards, which can be thousands of timesteps long, seems particularly daunting when compared to the direct association between inputs and targets found in supervised learning.
=> 강화학습은 보상을 기반으로 학습을 하나 보상을 받는 시점이 정해지지 않음. 이는 딥러닝과는 다름 - Another issue is that most deep learning algorithms assume the data samples to be independent, while in reinforcement learning one typically encounters sequences of highly correlated states.
=> 딥러닝은 변수들이 독립임을 가정하지만 강화학습에서 해결하고자 하는 데이터(시퀀스)가 높은 상관성을 가진채로 존재함 - Furthermore, in RL the data distribution changes as the algorithm learns new behaviours, which can be problematic for deep learning methods that assume a fixed underlying distribution.
=> 딥러닝은 fixed underlying function(확률분포)를 가정하지만 강화학습의 경우 distribution이 변화함.
논문에서는 위와 같은 문제점들을 극복하여 neural network를 RL(Q-learning)에 적용
Background
(optimal action value function)
\[\begin{aligned} Q^*(s,a) = \mathbb{E}[r + \gamma\underset{a`}{\text{max}}Q^*(s',a')|s,a] \end{aligned}\]state(s)와 action(a)에서의 optimal action value fuction. 이 함수를 가능한 정확히 근사해야 문제의 solution이 좋음
\[\begin{aligned} Q_{i+1}(s,a) = \mathbb{E}[r + \gamma\underset{a`}{\text{max}}Q_i(s',a')|s,a] \end{aligned}\]optimal action value function 개념적으로는 윗 식에서 $i $으로 iteration을 수없이 많이 iteration하여 얻을 수 있음. 그러나 이 방법은 실제 사용할 수 없는데 구현해야할 때에 수많은 state와 action을 table에서 s,a를 모두 저장해야 하기 때문이다.
(loss function of Q-network)
\[\begin{aligned} &L_i(\theta_i) = \mathbb{E}_{s,a}[(y_i - Q(s,a;\theta_i))^2]\\ &\text{where, } y_i = \mathbb{E}[r+\gamma \underset{a'}{\text{max}}Q(s',a';\theta_{i-1})] \end{aligned}\]따라서 위와 같이 Loss function을 정의하여 Neural network를 stochastic GD로 학습시켜서 Q값을 근사한다.

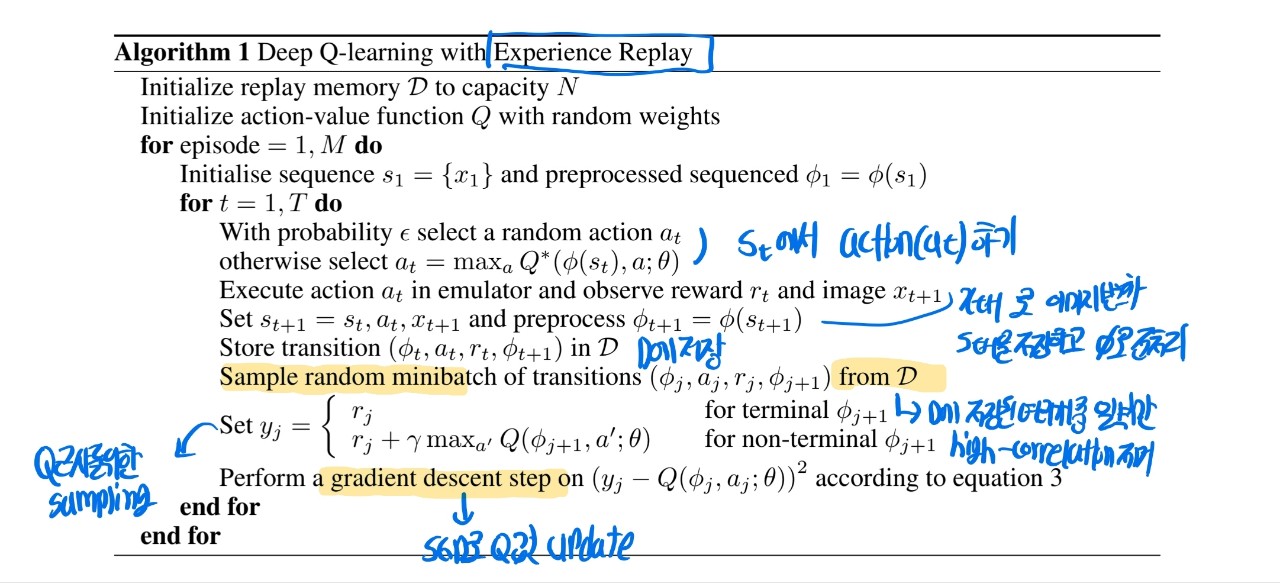
Deep Reinforcement Learning
experience replay
- store the agent’s experiences at each time-step, et = (st , at , rt , st+1 ) in a data-set D = e1 , …, eN
- During the inner loop of the algorithm, we apply Q-learning updates, or minibatch updates, to samples of experience, e ∼ D, drawn at random from the pool of stored samples.
- After performing experience replay, the agent selects and executes an action according to an -greedy policy.
algorithm